
Allergic Rhinitis
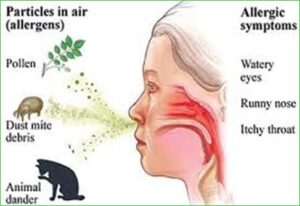 Allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose. If you have allergic rhinitis, your immune system mistakenly identifies a typically harmless substance is called an allergen. The immune system responds to the allergen by releasing histamine and chemical mediators that typically cause symptoms in the nose, throat, eyes, ears, skin and roof of the mouth.
Allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose. If you have allergic rhinitis, your immune system mistakenly identifies a typically harmless substance is called an allergen. The immune system responds to the allergen by releasing histamine and chemical mediators that typically cause symptoms in the nose, throat, eyes, ears, skin and roof of the mouth.
Allergic rhinitis can also be triggered by common indoor allergens such as the dried skin flakes, urine and saliva found on pet dander, mold, droppings from dust mites and cockroach particles. This is called perennial allergic rhinitis, as symptoms typically occur year-round. In addition to allergen triggers, symptoms may also occur from irritants such as smoke and strong odors, or to changes in the temperature and humidity of the air. This happens because allergic rhinitis causes inflammation in the nasal lining, which increases sensitivity to inhalants.
Many people with allergic rhinitis are prone to allergic conjunctivitis (eye allergy). In addition, allergic rhinitis can make symptoms of asthma worse for people who suffer from both conditions
Common symptoms of allergic rhinitis include:
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Stuffy nose
- Itchy nose
- Coughing
- Sore or Scratchy throat
- Itchy eyes
- Watery eyes
- Dark circles under the eyes


