
Conjunctivitis
 Allergic conjunctivitis is an eye inflammation caused by an allergic reaction to substances like pollen or mold spores.
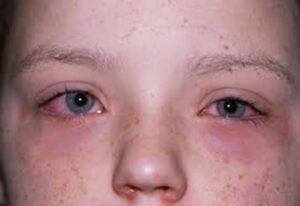
Allergic conjunctivitis is an eye inflammation caused by an allergic reaction to substances like pollen or mold spores.
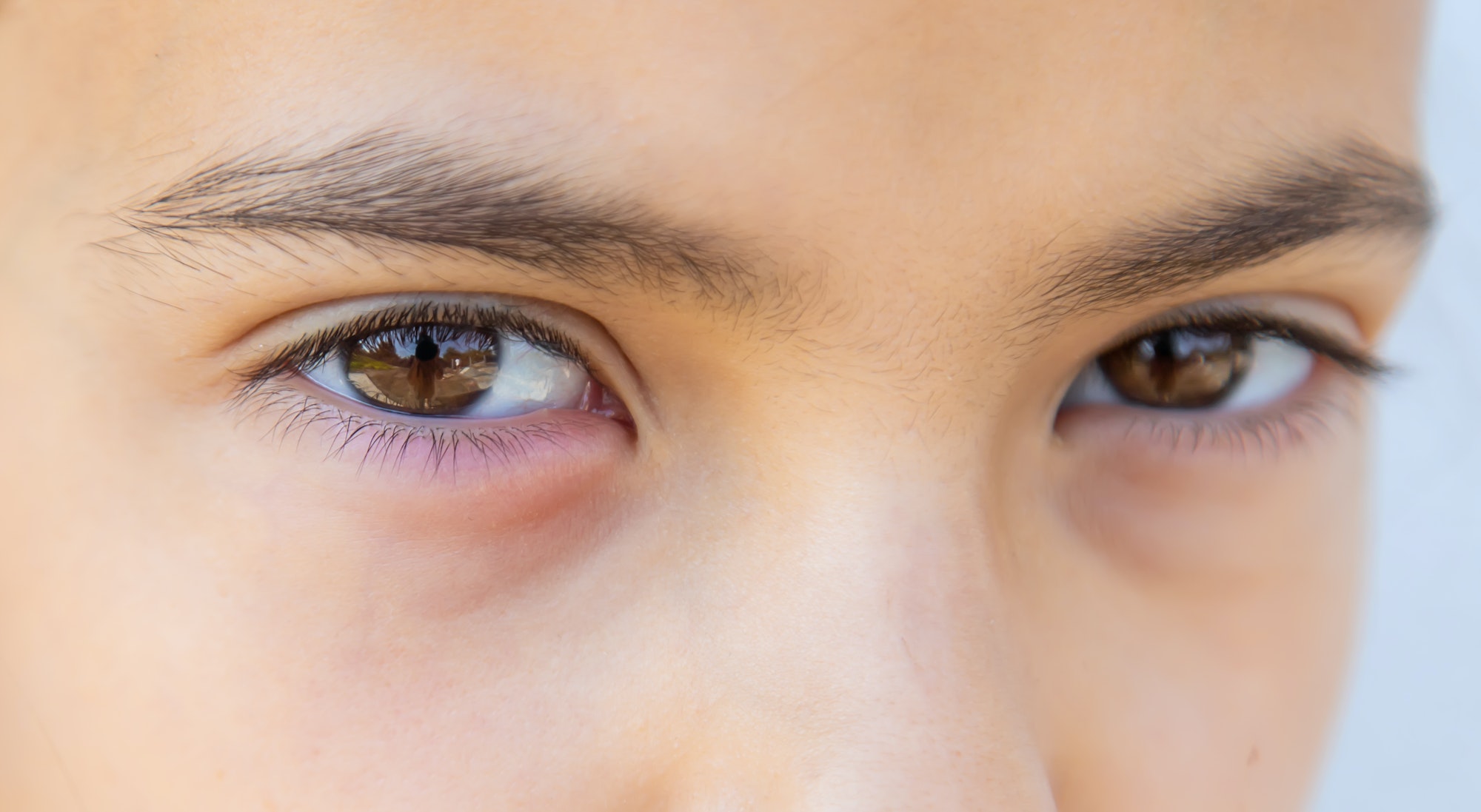
The inside of your eyelids and the covering of your eyeball have a membrane called the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva is susceptible to irritation from allergens, especially during hay fever season. Allergic conjunctivitis usually happens when a person’s eyes come into contact with an allergen, a substance that makes the body’s immune system overreact. The eye becomes sore and inflamed. Symptoms occur because the overreacting immune system makes the body release histamine and other active substances through mast cells. The blood vessels dilate, or expand, and this irritates the nerve endings. The result is an increased secretion of tears.
Symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis include:
- Red or pink eyes: The eyes become irritated as the capillaries, or small blood vessels, widen in the conjunctiva.
- Pain: This may affect one or both eyes. If a person has painful, red eyes, is sensitive to light, and their vision is affected, they should see a doctor at once.
- Itchiness: As the eyes are irritated, they may itch. Rubbing can make the itchiness worse.
- Swollen eyelids: The eyelids may puff up when the conjunctiva becomes inflamed, or if the person has been rubbing them a lot.
- Soreness: The inflammation may make the whole area feel sore and tender. Some people say the soreness feels like burning


